

A Bluetooth connection to your headphones – regardless of codec – is not lossless.īut high resolution is another matter. Oh, you’ll also need some decent wired headphones or in-ear monitors to enjoy the fruits of losslessness. Now, either of those is all that you need if all you want is lossless ALAC, rather than lossy AAC. Too old and it either won’t run 11.4, or will slow down too much for practical use. This is worth emphasising because many people use something like an old Mac Mini as a music server. If your device isn’t suitable for use with the current OS, you’re out of luck. Apple Music works with earlier versions, but you won’t be able to enable either lossless or high-resolution lossless audio.
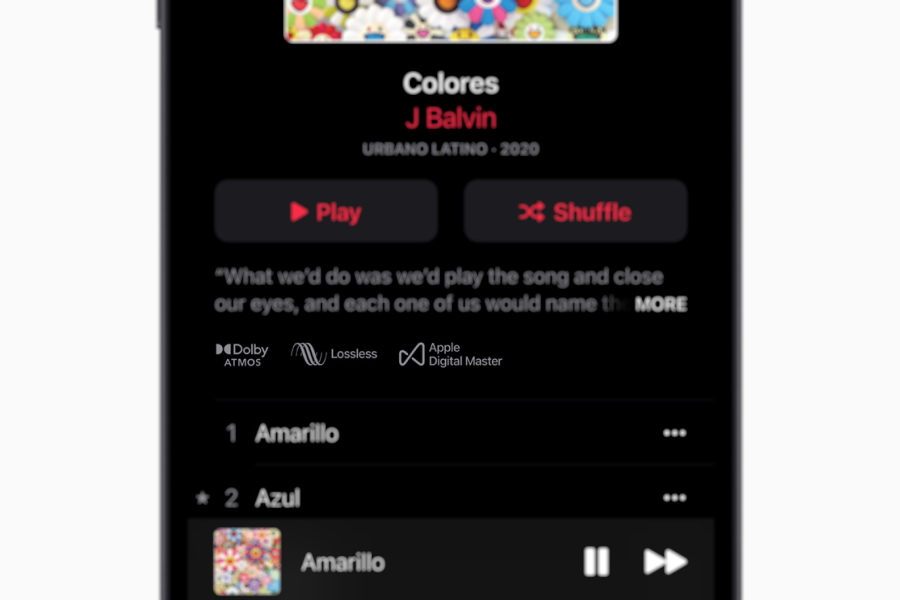
Your iPad or iPhone must be running at least what is, as I write, the newest version of iPadOS or iOS, 14.6, and your Mac must be running at least macOS 11.4. I’ll be looking at getting Apple Music high resolution lossless using an iPhone or iPad (pretty much the same) and a Mac. Yes, there is iTunes for Windows, but let’s not go there. In this article, I’m going to assume that you’re a user of Apple products. The compression is generally in the range of 40% to 60%. They typically require fewer bits of data than the original. These use a predictive model, so that the data stream only needs to be corrections to the predictions. The details differ, but I believe that the way ALAC works is much the same way that FLAC works … and also Dolby TrueHD and, to a lesser extent, DTS-HD Master Audio. The format Apple uses for its lossless streams is ALAC, otherwise known as Apple Lossless. Interestingly, Apple doesn’t charge more for lossless, nor for high resolution lossless. Not just lossless, but for some material at least, high resolution lossless with sampling frequencies of up to 192kHz. But since June 2021, Apple has provided lossless streaming. (That’s a compression of around 5:1.)Īpple has long maintained that there are no audible differences between such streams and the lossless original. As with iTunes, Apple Music used lossy compression, specifically AAC compressed to a 256kbps stream. Introduced in 2015, the emphasis has shifted strongly from the music-purchase model of iTunes, to a streaming service, à la Spotify. Perhaps it’s a bit late to the party, but those people who are both Apple users and audiophiles must now be thrilled that Apple Music is going lossless.įor those not familiar with it, Apple Music is both a music service, and an app which is the successor to the music portion of Apple iTunes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
